K Nearest Neighbours
This is the first Learning Algorithm, we will be talking about. K-Nearest Neighbours algorithm can be used both for regression and classification.

K-NN uses the concept of distance. So let us quickly define the term ‘distance’ here.
There can be many types of distance we can talk about like L1 norm, L2 norm, cosine similarity and many more.
We will be mostly using L2 norm which can be defined as follows.
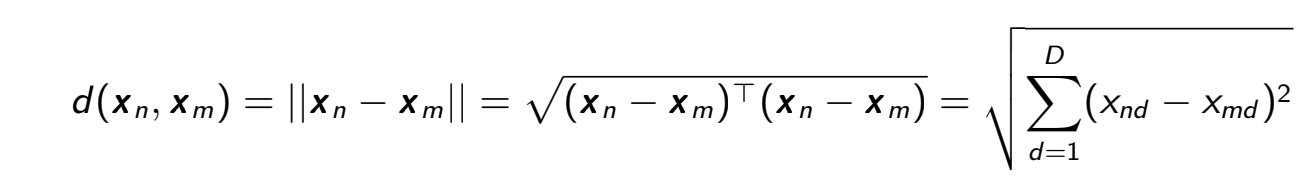
Task:
Given a supervised dataset, we have to predict the correct class whenever a new data comes.
Method :
Whenever a new data comes, its L2 distance from every other existing data is computed and we take the smallest K distances out of that.
We observe the class of each of the K nearest data points and the class with maximum count is assigned to the test data.
Let’s understand it through an example:
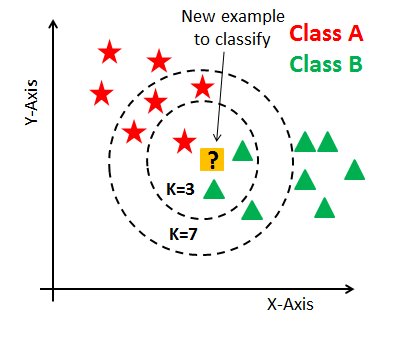
Initially, the value of K was chosen to be 3, so we took 3 nearest neighbors to that of the test data. Upon observation, we find out that 2 of the neighbors are from class B and one is from class A. Hence the test data is assigned to class B.
Now when we chose the value of K=7, the class assigned to the test data changes to class A.
Solution: We need to keep a validation dataset for the training to choose the right value of K.
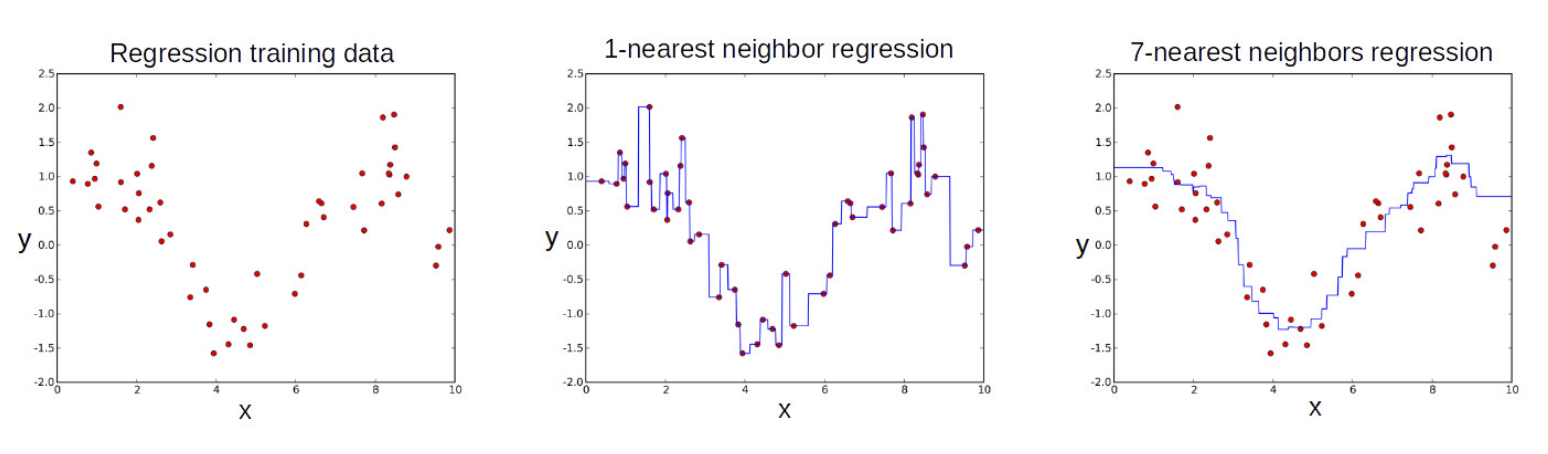
The example we took was for classification and we can also use KNN for regression purposes. One such idea would be to take the average of all the neighbor values and assign it as the output for the test data.
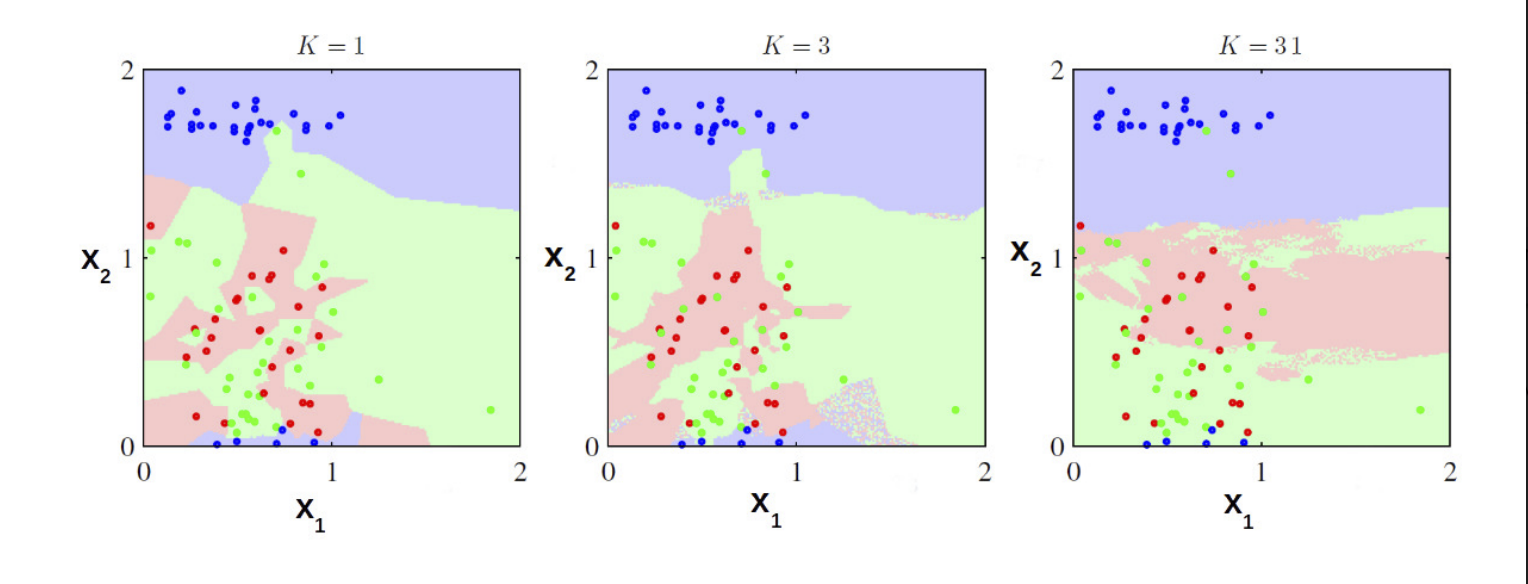
Note: The smoothness of the decision boundaries depends on the value of K chosen. Larger the value of K, smoother will be the decision boundary.
In the figure given below, we can see the effects of changing the value of K on classification and regression also.
The figure below is for regression:
KNN is expensive in terms of space and computation as you need to store the entire data for testing and for each test, you need to compute the distance of test data for each of the available data.
Keep Learning, Keep Sharing😊
